Delving into the worksheet heating curve of water answers, we embark on an enlightening journey that unveils the intricacies of water’s thermal behavior. This comprehensive guide delves into the concept of heating curves, exploring the distinct stages of water’s transformation from a solid to a liquid and gaseous state.
By unraveling the factors that influence this curve, we gain insights into the practical applications and analytical techniques employed in scientific and engineering fields.
Understanding the Heating Curve of Water: Worksheet Heating Curve Of Water Answers
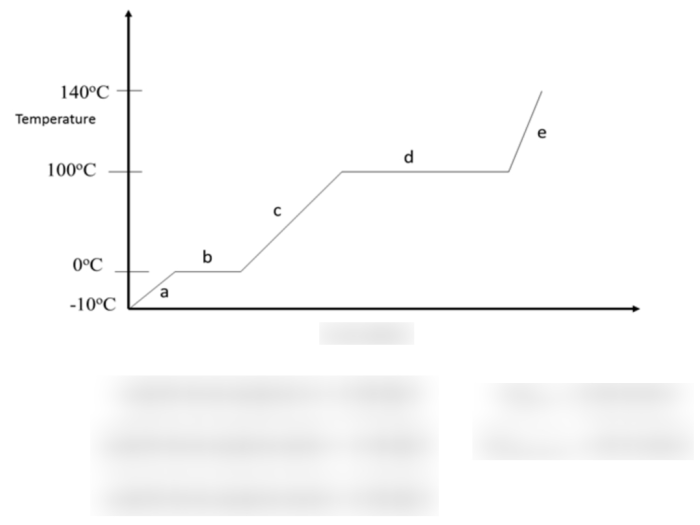
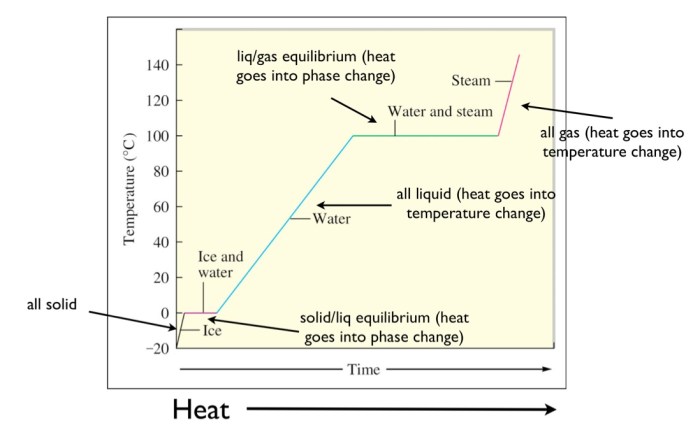
A heating curve is a graphical representation of the temperature of a substance as it is heated. The heating curve of water is a unique and distinctive curve that can be divided into several distinct stages.
The first stage of the heating curve of water is the liquid phase. In this stage, the temperature of the water increases as heat is added. The slope of the curve in this region is relatively constant, indicating a steady increase in temperature.
The second stage of the heating curve of water is the vaporization phase. In this stage, the temperature of the water remains constant as heat is added. This is because the heat is being used to convert the water from a liquid to a gas.
The vaporization phase ends when all of the water has been converted to steam.
The third stage of the heating curve of water is the gas phase. In this stage, the temperature of the steam increases as heat is added. The slope of the curve in this region is relatively constant, indicating a steady increase in temperature.
Factors Affecting the Heating Curve of Water, Worksheet heating curve of water answers
The heating curve of water can be affected by several factors, including pressure and impurities.
Pressure affects the heating curve of water by changing the boiling point of water. The higher the pressure, the higher the boiling point of water. This is because the increased pressure makes it more difficult for the water molecules to escape into the gas phase.
Impurities can also affect the heating curve of water. Impurities can lower the boiling point of water by providing nucleation sites for the formation of bubbles. This can cause the water to boil at a lower temperature than it would if it were pure.
Applications of the Heating Curve of Water
The heating curve of water is a useful tool in science and engineering. It can be used to determine the boiling point of water, to study the phase transitions of water, and to design heating and cooling systems.
In industry, the heating curve of water is used to control the temperature of processes. For example, in the food industry, the heating curve of water is used to control the temperature of cooking processes.
Analysis of the Heating Curve of Water
To measure the heating curve of water, an experiment can be designed using a thermometer and a heat source. The temperature of the water is measured as heat is added. The data from the experiment can be organized into a table and plotted on a graph.
The graph of the heating curve of water will show the three distinct stages of the heating curve: the liquid phase, the vaporization phase, and the gas phase.
FAQ Guide
What is the significance of the heating curve of water?
The heating curve of water provides insights into the energy changes and phase transitions that occur as water is heated. It allows scientists and engineers to understand the thermal behavior of water under different conditions.
How does pressure affect the heating curve of water?
Pressure can shift the temperature at which water undergoes phase transitions. Higher pressure generally leads to higher temperatures for these transitions.
What are some practical applications of the heating curve of water?
The heating curve of water finds applications in various fields, including power generation, refrigeration, and food processing, where understanding water’s thermal behavior is crucial for optimizing processes.