Select the correct statement s about fungal life cycles – Embarking on a comprehensive exploration of fungal life cycles, this discourse unveils the intricate mechanisms and diverse strategies employed by these ubiquitous organisms. From asexual reproduction to sexual encounters, and the profound influence of environmental factors, we delve into the fascinating world of fungi, unraveling their ecological significance and potential applications.
Fungi, a kingdom unto themselves, exhibit remarkable adaptability and resilience, playing pivotal roles in nutrient cycling, decomposition, and ecosystem dynamics. Their life cycles, characterized by distinct stages and reproductive strategies, offer a glimpse into the evolutionary marvels that have shaped their ecological dominance.
Define Fungal Life Cycles
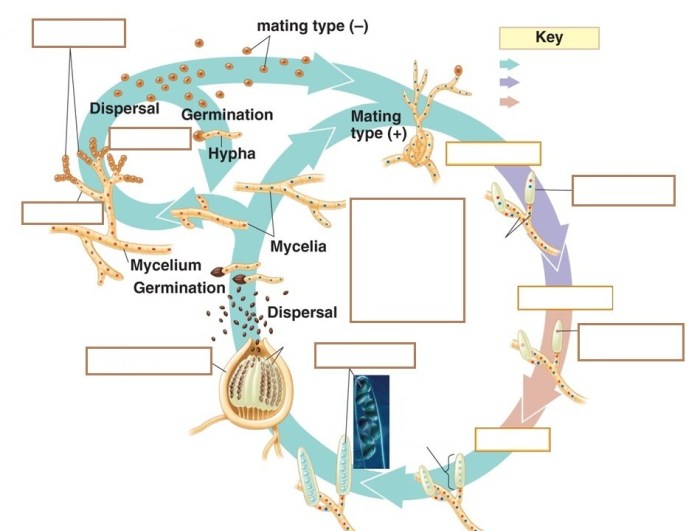
Fungal life cycles involve distinct stages of growth and reproduction, including spore production, germination, hyphal growth, and potential sexual reproduction. Fungi exhibit diverse life cycles, ranging from simple asexual reproduction to complex sexual cycles involving meiosis.
Asexual Reproduction: Select The Correct Statement S About Fungal Life Cycles
Asexual reproduction in fungi occurs through the production of spores, which are specialized cells that can develop into new individuals without the fusion of gametes. Common types of asexual spores include:
- Conidia: Produced on specialized structures called conidiophores.
- Sporangiospores: Contained within sporangia.
- Oidia: Fragmented pieces of hyphae.
- Budding: Formation of new individuals as outgrowths of existing hyphae.
Asexual reproduction offers benefits such as rapid population growth and adaptation to specific environments. However, it also limits genetic diversity and can lead to the accumulation of deleterious mutations.
Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction in fungi involves the fusion of gametes, resulting in the formation of a zygote. The zygote undergoes meiosis to produce haploid spores, which can then germinate and develop into new individuals.
Meiosis plays a crucial role in sexual reproduction by reducing the chromosome number by half, ensuring genetic diversity, and eliminating harmful mutations.
Fungi exhibit various mating systems, including:
- Homothallism: Self-fertilization within a single individual.
- Heterothallism: Requires the fusion of gametes from different individuals.
Environmental Factors Influencing Fungal Life Cycles
Environmental factors significantly influence fungal growth and reproduction. Temperature, moisture, and pH play crucial roles:
- Temperature: Fungi have specific temperature ranges for optimal growth and reproduction.
- Moisture: Water availability is essential for fungal growth and spore dispersal.
- pH: Fungi can tolerate a wide range of pH levels, but specific pH ranges are optimal for their life cycles.
Environmental factors can impact the duration and success of fungal life cycles. For instance, fungi that have adapted to specific environmental conditions, such as extreme temperatures or acidic environments, exhibit specialized adaptations to ensure their survival and reproduction.
Ecological Significance of Fungal Life Cycles

Fungal life cycles play a vital role in nutrient cycling and decomposition in ecosystems:
- Saprophytic fungi: Decompose organic matter, releasing nutrients back into the soil.
- Mycorrhizal fungi: Form symbiotic relationships with plants, enhancing nutrient uptake and stress tolerance.
Fungal life cycles contribute to ecosystem dynamics by influencing nutrient availability, soil structure, and plant growth. Additionally, fungi have potential applications in biotechnology and medicine, such as in the production of antibiotics and enzymes.
Expert Answers
What are the key stages involved in a fungal life cycle?
Fungal life cycles typically involve spore production, germination, hyphal growth, and, in some cases, sexual reproduction and spore formation.
How do asexual and sexual reproduction differ in fungi?
Asexual reproduction involves the production of spores from a single parent, while sexual reproduction requires the fusion of two compatible mating types, leading to genetic recombination.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of asexual reproduction in fungi?
Asexual reproduction allows for rapid population growth and adaptation to stable environments, but it limits genetic diversity and can lead to vulnerability to environmental changes.