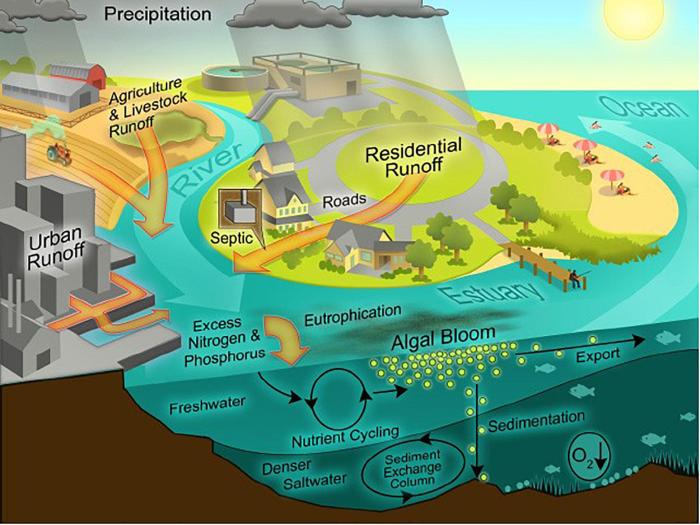
Eutrophication is the result of apex – Eutrophication, the enrichment of water bodies with nutrients, is a widespread environmental problem with severe ecological and economic consequences. This essay explores the role of apex predators in controlling eutrophication, highlighting their importance in maintaining aquatic ecosystem health.
Eutrophication occurs when excessive nutrients, primarily nitrogen and phosphorus, enter water bodies, leading to algal blooms and a decline in water quality. Apex predators, such as sharks, whales, and large fish, play a crucial role in regulating nutrient cycling and preventing eutrophication.
Eutrophication Definition
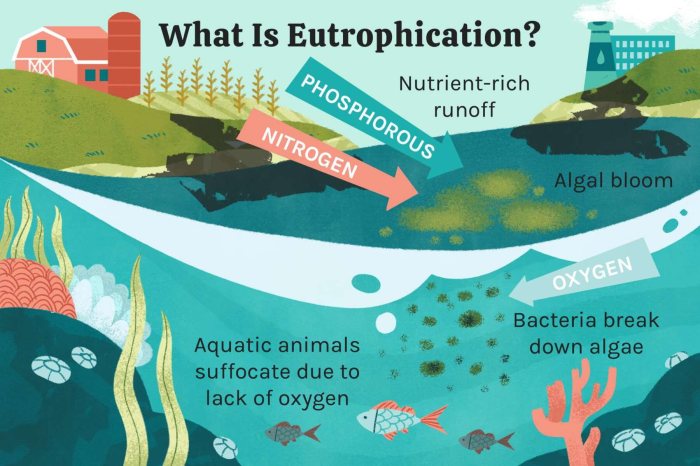
Eutrophication is a process that occurs when a body of water becomes enriched with nutrients, primarily nitrogen and phosphorus. This enrichment can lead to excessive growth of algae and other aquatic plants, which can have a range of negative ecological and socioeconomic consequences.
The primary sources of eutrophication include agricultural runoff, sewage discharge, and industrial effluents. These sources contribute excess nutrients to water bodies, which can stimulate algal blooms and disrupt the natural balance of the ecosystem.
Impacts of Eutrophication
Ecological Effects, Eutrophication is the result of apex
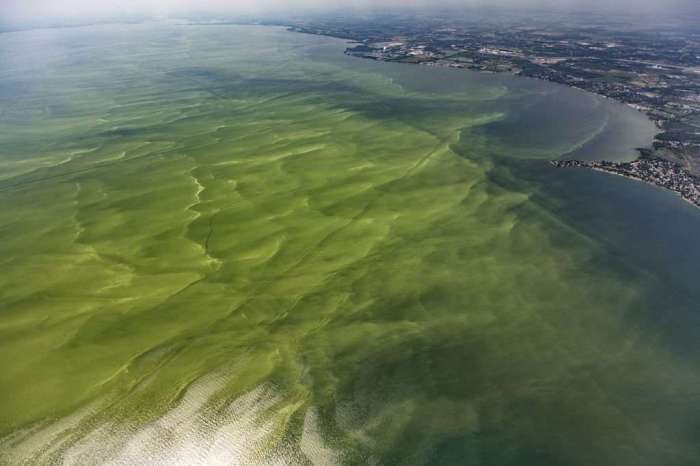
Eutrophication can have a range of negative ecological effects, including:
- Depletion of dissolved oxygen, which can lead to fish kills and other aquatic life mortality
- Alteration of food webs, as excessive algal growth can disrupt the balance of predator-prey relationships
- Loss of biodiversity, as eutrophication can favor certain species over others, leading to a decline in species richness
Economic and Social Consequences
Eutrophication can also have significant economic and social consequences, such as:
- Impaired drinking water quality, as algal blooms can release toxins and make water unsafe for consumption
- Reduced recreational value of water bodies, as excessive algal growth can make swimming, fishing, and boating less enjoyable
- Economic losses for fisheries and aquaculture, as eutrophication can reduce fish populations and harm shellfish beds
Mitigation and Management Strategies
There are a variety of methods that can be used to mitigate eutrophication, including:
- Reducing nutrient inputs from agricultural sources, such as implementing best management practices (BMPs) to minimize fertilizer runoff
- Upgrading wastewater treatment facilities to remove nutrients from sewage
- Implementing stormwater management practices to capture and treat runoff before it enters water bodies
- Restoring wetlands, which can act as natural filters to remove nutrients from water
However, managing eutrophication can be challenging due to the complex interactions between nutrients, algae, and other aquatic organisms. Additionally, the effectiveness of mitigation strategies can vary depending on the specific characteristics of the water body and the surrounding watershed.
Role of Apex Predators
Apex predators, such as sharks, whales, and large carnivorous fish, play an important role in controlling eutrophication.
Apex predators consume large numbers of smaller fish and other aquatic organisms, which helps to keep populations of these prey species in check. This, in turn, reduces the amount of nutrients available for algae to grow, which can help to mitigate eutrophication.
Case Studies

There are a number of successful case studies of eutrophication management efforts. One example is the Chesapeake Bay Program, which has been working to reduce nutrient pollution in the Chesapeake Bay since the 1980s. The program has implemented a variety of measures, including reducing fertilizer runoff from farms, upgrading wastewater treatment plants, and restoring wetlands.
As a result of these efforts, the Chesapeake Bay has shown significant improvements in water quality, with reduced algal blooms and increased fish populations.
Future Research Directions
There are a number of areas where further research on eutrophication is needed. These include:
- Developing more effective methods for reducing nutrient inputs from agricultural sources
- Improving the understanding of the role of apex predators in controlling eutrophication
- Developing new technologies for monitoring and managing eutrophication
By continuing to research and address the issue of eutrophication, we can help to protect the health of our water bodies and the ecosystems they support.
FAQ Summary: Eutrophication Is The Result Of Apex
What is the primary cause of eutrophication?
Excessive nutrient inputs from agricultural runoff, sewage discharge, and industrial effluents.
How do apex predators contribute to eutrophication control?
By consuming nutrient-rich prey, such as planktivorous fish, and regulating nutrient cycling through excretion.
What are the ecological consequences of eutrophication?
Loss of biodiversity, impaired water quality, and reduced ecosystem productivity.
What are the economic and social consequences of eutrophication?
Increased drinking water treatment costs, reduced tourism revenue, and diminished recreational opportunities.